When it comes to gaming or graphic-intensive tasks, one term you’ll often hear is VRAM. But what is VRAM exactly, and why is it so crucial?
VRAM, or Video Random Access Memory, is specialized memory that handles graphics-related tasks, ensuring smooth visuals and faster performance.
Different types of VRAM are optimized for various functions, from gaming to professional 3D rendering. Understanding how these types impact performance can help you choose the best option for your needs.
Let’s take a closer look at the 5 types of VRAM and how they enhance your device’s capabilities!
Key Takeaways
- VRAM enhances graphics performance by storing visual data for your GPU, ensuring smooth rendering for gaming and video editing.
- Different types of VRAM, such as GDDR and WRAM, provide various advantages like higher bandwidth or parallel processing for faster performance.
- Higher VRAM capacity allows for better handling of high-resolution textures, reducing lag and improving visual quality during intensive tasks.
- When VRAM runs out, your system resorts to slower system RAM, causing stuttering, lower resolution, and slower overall rendering speeds.
- Optimizing VRAM through driver updates, adjusting graphics settings, and closing unnecessary apps can significantly boost your system’s performance.
Table of Contents
What is VRAM?
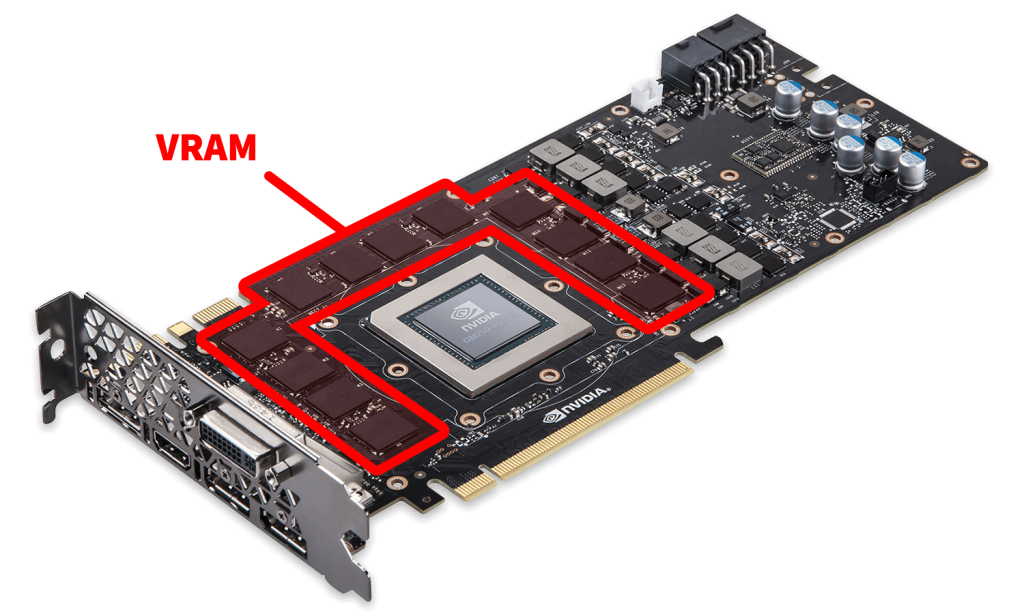
VRAM, or Video Random Access Memory, is a specialized type of memory found in graphics cards. It stores the image data that your computer needs to render, ensuring smooth and high-quality visuals for tasks like gaming and video editing.
Unlike regular RAM, which your CPU uses, VRAM is specifically designed to work with your GPU (Graphics Processing Unit).
The GPU accesses large amounts of data stored in VRAM quickly, reducing latency and allowing for high-performance graphics rendering.
How VRAM Works
VRAM, or Video Random Access Memory, is designed to store image data for your GPU. This helps your computer display high-quality visuals quickly.
Unlike regular RAM, VRAM is optimized to handle large amounts of graphic data at high speed. It allows for smooth rendering of high-resolution textures, 3D models, and animations.
VRAM and GPU Connection
VRAM connects directly to the GPU, giving it quick access to the stored graphic data. This speeds up loading times and boosts performance.
With VRAM, the GPU doesn’t need to use slower system RAM, preventing lags and ensuring a smooth experience. The GPU pulls textures and visual elements from VRAM to render scenes in real-time.
VRAM’s Role in Real-Time Rendering
VRAM stores critical elements like textures and shadows. These help the GPU render images or animations faster.
Not enough VRAM leads to stuttering, low-quality visuals, and longer load times. Tasks like gaming and video editing rely on VRAM to ensure smooth performance.
Parallel Architecture in VRAM
VRAM’s parallel architecture allows it to read and write data at the same time. This means faster processing for complex visuals.
This parallel setup improves memory bandwidth, making VRAM essential for demanding tasks like 4K gaming and 3D rendering.
VRAM Bandwidth and Data Transfer
VRAM’s performance depends on its bandwidth, which measures how fast it transfers data to the GPU. Higher bandwidth means faster processing of large files, like 4K textures.
This speed ensures that your system can handle complex visuals without slowing down. Gaming, video editing, and 3D modeling benefit from VRAM’s high bandwidth.
VRAM as a Buffer for the GPU
VRAM serves as a buffer for the GPU, holding data so the GPU doesn’t need to fetch it from system RAM. This prevents bottlenecks and keeps performance smooth.
Without this buffer, you’d see more stuttering and graphical glitches during intensive tasks. VRAM keeps your GPU working efficiently.
What Happens When VRAM Runs Out?
When VRAM is full, your system offloads graphic data to system RAM, which is slower. This causes frame drops, lower resolution, and slower rendering.
Upgrading your VRAM ensures your system can handle modern games and graphic-heavy tasks without performance issues.
5 Types of VRAM
VRAM is crucial for graphics performance, and there are different types with unique features. Knowing the differences helps you choose the right one for your system.
Let’s discuss the 5 types of VRAM:
| Type of VRAM | Key Features | Ideal Use |
|---|---|---|
| Window RAM (WRAM) | Dual ports for simultaneous read/write, 25% faster than standard VRAM | High-resolution graphics (e.g., 1,600 x 1,200) |
| SGRAM | Synchronized with GPU clock, handles multiple data pages at once | 3D rendering, gaming |
| Rambus DRAM (RDRAM) | High-speed (up to 800 MHz), used in older systems | Early gaming systems, workstations |
| Multibank DRAM (MDRAM) | Multiple memory banks for parallel data access, cost-effective | High-speed data processing at lower cost |
| GDDR (Graphics DDR) | High bandwidth, latest versions (GDDR6) offer faster speeds and power efficiency | Modern gaming, video editing, 3D rendering |
1. Window RAM (WRAM)
WRAM is a high-performance type of VRAM. It has dual ports that allow reading and writing at the same time, making it faster by 25% compared to standard VRAM.
It’s great for handling high-resolution graphics, like 1,600 x 1,200 pixels. WRAM is commonly used in professional displays and offers better performance at a lower cost.
2. Synchronous Graphics RAM (SGRAM)
SGRAM is designed to run in sync with the GPU’s clock speed. This makes it faster for 3D rendering and gaming.
SGRAM can handle multiple data pages at once, improving speed and performance during graphics-heavy tasks. It’s a cost-effective option for modern GPUs.
3. Rambus Dynamic RAM (RDRAM)
RDRAM was a high-speed VRAM used in older gaming systems and workstations. It could transfer data at speeds of up to 800 MHz, making it faster than other types at the time.
Though it’s no longer widely used due to cost, it helped push VRAM technology forward. RDRAM is a key part of VRAM history, offering faster data transfers in its era.
4. Multibank Dynamic RAM (MDRAM)
MDRAM splits memory into small banks that can be accessed independently. This parallel structure speeds up data processing.
It’s a more affordable option for systems that need high-speed performance. MDRAM is ideal for applications that require fast memory access without the high cost of other options.
5. GDDR (Graphics Double Data Rate) VRAM
GDDR is the most common VRAM used in modern GPUs. It has high bandwidth and is perfect for gaming, video editing, and other graphics-heavy tasks.
The latest version, GDDR6, offers faster speeds and improved power efficiency. GDDR continues to evolve, providing better performance with each generation.
How To Check VRAM
Knowing how much VRAM your system has is important for optimizing gaming, video editing, or any graphics-intensive tasks. Checking your VRAM is quick and easy, no matter which operating system you use.
How to Check VRAM on Windows
- Open Settings
Click on the Start button, then select Settings (the gear icon). - Go to System
Once in the settings menu, click on System and then select Display. - Advanced Display Settings
Scroll down and click on Advanced display settings to view more details. - Display Adapter Properties
Click on Display adapter properties at the bottom of the window. A new window will pop up showing details about your graphics card. - Check VRAM
Under the Adapter tab, look for Dedicated Video Memory. This is your VRAM.
How to Check VRAM on macOS
- Click on the Apple Icon
Click the Apple logo in the upper-left corner of your screen. - Select About This Mac
From the dropdown, select About This Mac. - Click on Displays
In the Overview tab, click on Displays to see information about your screen and VRAM. - Check Graphics Card Info
You will see the name of your graphics card along with the amount of VRAM available.
How to Check VRAM via Command Line (Linux)
- Open Terminal
PressCtrl + Alt + Tto open the terminal. - Enter Command
Type the following command:lspci -v | grep -A 12 VGAand hit enter. - Check VRAM Information
Scroll through the output to find your VRAM listed under preallocated memory or framebuffer size.
VRAM in Gaming and Video Editing
VRAM plays a critical role in both gaming and video editing by handling large amounts of graphic data. The right amount of VRAM ensures smoother gameplay and faster rendering times in creative tasks.
VRAM for Gaming
In gaming, VRAM stores textures, models, and other assets required for the GPU to render scenes. For 1080p gaming, 4GB of VRAM is usually enough, but for 4K or VR gaming, you’ll need 8GB or more.
If your VRAM is insufficient, you may experience lower frame rates, texture pop-ins, and reduced image quality. Having more VRAM allows you to run games at higher settings without performance issues.
VRAM for Video Editing and 3D Rendering
In video editing and 3D rendering, VRAM ensures smooth playback and fast processing of high-resolution footage. Projects in 4K or higher demand more VRAM, with 8GB or more recommended for 4K video editing.
Lack of VRAM in these tasks can cause slow rendering times and lag during real-time playback. With enough VRAM, you can work more efficiently, preview effects instantly, and reduce the time spent on exports.
Balancing VRAM for Both
For gamers who also engage in video editing or 3D rendering, balancing your VRAM needs is essential. Aim for 8GB or higher to handle both tasks seamlessly without compromising performance.
Investing in more VRAM will allow your system to run games smoothly while also efficiently handling video projects and 3D designs. This ensures better performance for all your graphic-intensive tasks.
VRAM vs. RAM: Key Differences You Need to Know
Understanding VRAM and RAM is essential for optimizing your computer’s performance. Both components serve vital roles, but their functions are distinct.
The table below breaks down their core differences, helping you decide which memory type is more important for your needs:
| Aspect | RAM | VRAM |
|---|---|---|
| What is it? | Temporary memory for system tasks | Specialized memory for storing graphical data |
| Primary Function | Enables multitasking and fast data access | Powers high-quality graphics and real-time image rendering |
| Used By | CPU (Central Processing Unit) | GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) |
| Performance Impact | More RAM improves multitasking and app speed | More VRAM boosts gaming and video rendering performance |
| Upgradability | Replaceable and upgradeable in most systems | Typically soldered onto the graphics card, not easily upgraded |
| Common Usage | General applications like browsing, productivity apps | Gaming, video editing, and other graphics-heavy tasks |
| Impact on Speed | Faster RAM helps system responsiveness | Faster VRAM enhances frame rates and visual quality |
| Capacity Range | Typically 4GB to 64GB or more | Usually 4GB to 24GB in high-end GPUs |
5 VRAM Optimization Tips
Optimizing your VRAM can significantly improve your computer’s performance, especially for gaming and video rendering tasks.
Let’s explore five simple yet effective ways to ensure your VRAM is working at its best:
1. Graphics Driver Update
Updating your graphics driver is crucial for VRAM optimization. New drivers often include performance improvements and bug fixes that maximize your GPU’s potential.
2. Tweaking the In-Game Graphics Settings
Lowering in-game settings like shadows, textures, and resolutions can reduce VRAM usage. Adjust these settings to strike a balance between visuals and performance.
3. Closing Unnecessary Resource-hungry Apps & Background Processes
Running too many applications can eat into your VRAM. Close unnecessary apps and processes to free up memory for graphics-intensive tasks.
4. Tracking Your VRAM Usage
Monitoring your VRAM usage helps you understand how much memory is consumed. Use built-in system tools or third-party software to track it in real-time.
5. Clearing Out Temporary Files
Temporary files can clog up your system and affect VRAM performance. Regularly clean these files to keep your computer running smoothly.
How To Increase VRAM
Boosting your VRAM can improve your computer’s performance, especially for gaming and video editing.
While upgrading physical VRAM isn’t always possible, here are simple ways to optimize what you have:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Adjust VRAM in BIOS | Allocate more VRAM by accessing BIOS and adjusting memory settings. |
| Increase Paging File Size | Use virtual memory by increasing your system’s paging file size. |
| Lower Graphics Settings | Reduce textures, shadows, and resolution to free up VRAM for better performance. |
| Update Graphics Drivers | Keep drivers updated for better VRAM management and performance. |
| Close Unused Apps | Free up VRAM by closing background apps and processes. |
1. Adjust VRAM in BIOS
In some systems, you can allocate more VRAM in the BIOS. Access the BIOS during startup, go to Advanced or Graphics settings, and increase the VRAM allocation—usually from 128MB to 256MB or 512MB.
2. Increase Paging File Size
If VRAM runs out, a larger paging file can act as virtual memory. Adjust your system’s paging file size to give more room for memory-heavy tasks.
3. Lower Graphics Settings
Reduce texture quality, shadows, and resolution to free up VRAM. This prevents overloading the GPU and helps improve performance.
4. Update Graphics Drivers
Keeping your graphics drivers up to date ensures better VRAM management. New drivers often come with performance enhancements that maximize VRAM efficiency.
5. Close Unused Apps
Close background apps that use VRAM. This frees up memory for more important tasks, like rendering visuals in games or creative software.
Choosing the Right VRAM for Your Needs
Selecting the right amount of VRAM is crucial for maximizing your system’s performance. Whether you’re a gamer, video editor, or casual user, choosing the right VRAM depends on how you use your computer.
1. Gaming Needs
For gaming, more VRAM ensures smoother gameplay and better graphics. If you’re playing modern AAA games at high resolutions, 6GB to 8GB of VRAM is recommended for optimal performance.
2. Video Editing and 3D Rendering
For video editing and 3D rendering, VRAM plays a significant role in handling complex visuals. Professionals should aim for 8GB or more to handle 4K video editing or detailed 3D models efficiently.
3. General Computing
For basic tasks like web browsing, video streaming, and office work, VRAM isn’t a critical factor. Integrated GPUs with 2GB to 4GB of VRAM are more than enough for everyday computing needs.
4. Future-Proofing Your System
If you want to future-proof your system, consider going for more VRAM than you currently need. An 8GB VRAM card will handle new software demands and higher-resolution displays for years to come.
Conclusion
VRAM plays a crucial role in enhancing your computer’s graphics performance, especially for gaming, video editing, and rendering tasks.
By understanding the different types of VRAM and how they function, you can make informed choices that optimize your device’s capabilities.
Choosing the right VRAM depends on your specific needs, whether you’re a gamer, creative professional, or casual user. Ensuring your system has enough VRAM can lead to smoother visuals and faster processing.
Stay informed, and make the most of your system’s potential for better graphics and performance!
Want to Make the Most of Your VRAM?
Find valuable resources in our TMGVoice blog collection on hardware upgrades, and see how TMGVoice.com can help enhance your graphics performance.
Begin exploring today!
FAQ
What is VRAM in a Graphics Card?
VRAM is video memory that stores image data for faster rendering by the GPU.
Is VRAM the Same as RAM?
No, VRAM is dedicated to graphics processing, while RAM handles general system tasks.
Is VRAM Used for Gaming?
Yes, VRAM is crucial for rendering high-quality graphics in gaming.
How Much VRAM Do I Need?
For modern games, 4-8GB of VRAM is generally sufficient, but demanding titles may require more.