Even though we have fiber optic and cable internet, DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) still provides internet for about a third of broadband users in the U.S. It uses old telephone lines to deliver high-speed internet. This means you can get fast internet without extra cables.
When looking at internet options, know what DSL offers compared to fiber optic and cable. Understanding DSL’s pros and cons helps you choose the best internet for streaming, working, or web browsing.
In this article, we will go over what DSL means, how they work, their pros and cons, and many more.
Let’s get right into it.
Key Takeaways
- DSL uses existing telephone lines for broadband, so no new wiring is needed.
- It’s widely available, especially where fiber optic hasn’t reached yet.
- It’s essential to compare DSL with fiber optic and cable to find what fits your needs.
- Telecom companies still support DSL, offering it as an option alongside newer technologies.
- Knowing your internet needs is key to deciding if DSL’s lasting power is enough or if it’s time to switch.
Table of Contents
What is DSL (Digital Subscriber Line)?
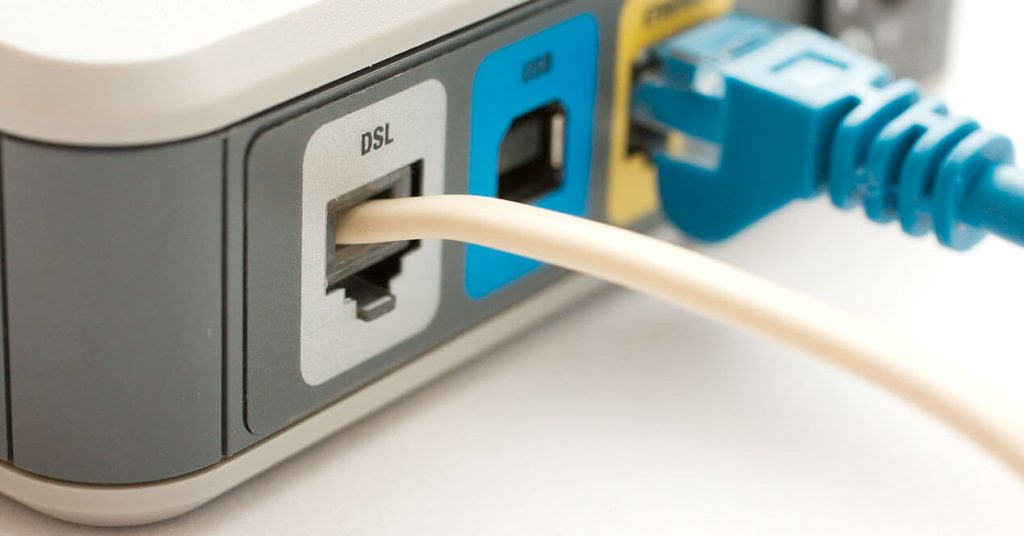

Digital Subscriber Line (DSL), formerly known as Digital Subscriber Loop, is a type of high-speed internet connection that utilizes the existing copper telephone lines to transmit data. Unlike traditional dial-up connections, DSL allows simultaneous use of the internet and telephone services, making it a more efficient and user-friendly option.
DSL is a high-speed internet choice that doesn’t cost too much. It’s great for places without a lot of fiber-optic networks. DSL’s advantage is that it’s everywhere you find phone lines. The technology has gotten better over time, making it faster and more reliable.
Choosing DSL is smart because setting it up is easy. You just need a DSL modem and a few steps to start. This makes using DSL simple from day one.
- High-speed internet access can be readily achieved through a standard telephone line.
- A DSL modem is necessary to translate digital signals from the computer to the DSL line.
- The continued reliance on DSL service by leading internet service providers to cater to a broad customer base.
How DSL works?
DSL technology works by using existing telephone lines to transmit data. Unlike traditional phone services, DSL doesn’t tie up the line. It divides the line’s frequency so you can talk and surf the web at the same time. This smart design is what makes DSL modems so special.
Asymmetric DSL (ADSL) is mostly for home use. It gives faster downloading speeds than uploading. This is because people usually get more information from the internet than they send to it. On the other hand, symmetric DSL (SDSL) provides equal speeds for both. This is perfect for businesses that need to send out large amounts of data too.
DSL modems change analog signals into digital ones. This lets your device understand the data. This process allows DSL to use lines made for voice calls. Also, thanks to better technology, DSL speeds are now much faster. Now, we can enjoy quick internet without changing our phone setup.
7 types of DSL
Understanding the different DSL technologies is key for anyone looking into DSL services. The tech world changes fast, and so do DSL internet services. Depending on whether it’s for home or business, choosing the right DSL matters.
It affects download and upload speeds and overall net efficiency. Let’s look closer at each DSL type and what makes them unique.
| Type of DSL | Download Speeds | Upload Speeds | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|---|
| ADSL | High | Lower than Download | General Consumers |
| HDSL | Symmetrical | Symmetrical | Business Users |
| SDSL | Symmetrical | Symmetrical | Business Users |
| VDSL | Very High | High | Entertainment & Gaming |
| SHDSL | Stable | Stable | Business Users |
| VDSL2 | Higher than VDSL | High | Multimedia Applications |
| G.fast | Near Fiber-Optic | Near Fiber-Optic | Fiber-Like Speed Seekers |
1. Asymmetric DSL (ADSL)
ADSL is a very common DSL type. It’s made for faster downloads than uploads. This is great for most internet users who enjoy streaming videos, surfing the web, and downloading content. ADSL providers have various packages to match what users need.
2. High-Bit-Rate DSL (HDSL)
HDSL was among the first DSL types, aimed at equal upload and download speeds. It’s more for businesses needing steady uploads for things like video calls and large transfers.
3. Symmetric DSL (SDSL)
SDSL, similar to HDSL, gives equal upload and download speeds. It’s chosen by businesses and serious users who need strong internet for sending and receiving data. SDSL is all about consistent, high-speed internet use.
4. Very High-Bit-Rate DSL (VDSL)
VDSL is great for those close to DSL equipment. It offers much faster speeds than ADSL or SDSL. For high-def streaming and gaming that need top-notch internet, VDSL is a strong choice.
5. Single-Pair, High-Speed DSL (SHDSL)
SHDSL is a business-oriented version of HDSL. It offers even upload and download speeds over a single copper wire pair. SHDSL meets the needs of firms with lots of data going both ways.
6. Very-High-Bit-Rate 2 (VDSL2)
VDSL2 improves upon VDSL, reaching longer distances with better speeds. It’s becoming popular in places without fiber optics, but quick connections are still needed.
7. G.fast
G.fast is a cutting-edge DSL type, nearing fiber-optic speeds on old phone lines. It’s pushing the limits of what DSL can do.
Importance of DSL in the Modern World
In the wide world of internet connectivity, Digital Subscriber Lines (DSL) really stand out. They provide fast, reliable high-speed broadband internet access to many. DSL uses existing phone lines to connect people to the internet, making it easy to set up and widely available.
DSL has stayed important, even as new technologies emerge. It’s because it doesn’t need much new infrastructure to start. It also meets the internet needs of homes and small businesses very well.
- DSL is key in places where high-speed internet is rare or too expensive.
- It’s important for a service provider who wants to use existing copper lines wisely.
- For users, DSL’s benefits like affordability and steady speeds, make it a good option, especially when other choices like fiber are not available or too costly.
Even with new tech coming out, DSL keeps proving its worth. It adapts to what people worldwide need from their internet. DSL ensures we all can stay connected, showing its lasting value in our connected lives.
7 Advantages of DSL
Exploring the benefits of a DSL internet connection is key to understanding why it’s still popular. It uses existing telephone wiring, making it a top choice for internet users. Here’s why DSL is still seen as reliable and relevant across the country.
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Broad Availability | DSL’s widespread availability benefits users, as most homes and businesses already have telephone wiring in place, simplifying the setup process with a DSL modem. |
| Cost-Effective | DSL offers an affordable internet option, leveraging existing telephone infrastructure to reduce costs for both users and providers. |
| Dedicated Connection | DSL provides users with a dedicated internet connection, ensuring consistent performance and avoiding slowdowns during peak usage periods. |
| Always-On Connection | DSL offers an always-on connection, eliminating the need to dial in for internet access and providing instant connectivity through an ethernet cable. |
| Faster Speeds | Compared to dial-up, DSL delivers faster download speeds, smoother video streaming, and quicker browsing experiences, marking a significant improvement. |
| Simultaneous Use | With DSL, users can simultaneously use the phone and internet, as the service splits the line between voice and data, allowing uninterrupted communication and browsing. |
| Stable Performance | DSL ensures stable performance, even under high demand, which is crucial for activities like video calls and online gaming that require consistent bandwidth. |
1. Broad Availability
DSL’s wide reach is one of its top perks. Since most homes and businesses already have existing telephone wiring, getting DSL is often easy. Just sign up and connect a DSL modem. This makes it a go-to choice, especially where other internet options are scarce.
2. Cost-Effective
DSL offers an affordable way to get online. Using existing telephone wiring cuts down costs for users and providers alike. Hence, DSL stands out as a cost-friendly option.
3. Dedicated Connection
A dedicated connection with DSL means smooth and consistent internet. This is great for both work and play. You won’t face slowdowns during busy hours thanks to this dedication.
4. Always-On Connection
DSL’s always-on connection means no more dial-up delays. You’re ready to browse anytime without needing to log in. This convenience comes via an ethernet cable, linking you directly to speedy service.
5. Faster Speeds Than Dial-Up
Compared to dial-up internet, DSL speeds are a game-changer. It offers faster downloads, smooth video streams, and quick browsing. This is a big leap forward for those used to dial-up.
6. Simultaneous Use of Phone and Internet
With DSL, you can use the phone to browse at the same time. It splits the line between voice and data. So there are no disruptions to calls or online activities.
7. Stable Performance
DSL ensures steady performance, even with high demand. This stability is crucial for video calls, online games, and other tasks needing constant bandwidth. It keeps disruptions at bay.
5 Disadvantages of DSL
DSL internet is easy to get and affordable for many, but it has its drawbacks. Knowing these can help anyone thinking about using DSL for the internet. It’s especially important for those who see it as their main choice.
| Disadvantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Distance Limitations | DSL’s main challenge lies in how distance impacts connection speeds, with greater distances resulting in weaker DSL speeds due to limitations in signal strength. |
| Speed Variability | DSL users may experience fluctuations in internet speed due to factors like distance and network traffic, leading to inconsistent performance that can affect online activities such as work and gaming. |
| Limited Bandwidth | DSL’s reliance on old phone lines imposes constraints on its bandwidth capacity, limiting the amount of data it can handle simultaneously, which may pose challenges for households or businesses with high internet usage demands. |
| Dependence on Phone Lines | The performance of DSL is tied to the condition of existing phone lines, which may not always be optimal, particularly in areas where infrastructure has not been updated, thus restricting the potential of DSL services. |
| Limited Availability of High Speeds | While DSL allows concurrent use of phone and internet services, not all areas can access the fastest speeds due to infrastructure limitations, resulting in disparities in high-speed DSL availability across regions. |
1. Distance Limitations
DSL’s big challenge is how distance affects connection speeds. The farther away you are from the provider’s setup, the weaker your DSL speed gets. This is something DSL companies can’t easily fix.
2. Speed Variability
DSL users might see their internet speed go up and down. This isn’t just because of distance. The amount of traffic on the network can also change how fast your internet is, making it hard to work or play online smoothly.
3. Limited Bandwidth
The way DSL uses old phone lines means there’s only so much data it can handle at once. For homes or businesses that need to do a lot involving the internet, this limited bandwidth could be a problem. Especially if many users or big tasks are all happening at the same time.
4. Dependence on Phone Lines
Since DSL depends on old phone lines, its performance can be limited. In some places, these phone lines haven’t been updated. So, DSL providers must work with what’s already there, which might not be the best for newer tech needs.
5. Limited Availability of High Speeds
Even though DSL lets you use the phone and internet together without issues, not everyone can get the fastest speeds. Some areas just don’t have the infrastructure for top-speed DSL. This means providers can’t always offer the best high-speed options everywhere.
Comparing DSL with Other Internet Options
Sure, here’s a comparison of DSL with other internet options in table format:
| Aspect | DSL | Cable Internet | Fiber-Optic Internet | Satellite Internet |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Availability | Widely available, especially in urban and suburban areas, but may be limited in rural regions | Widely available in urban and suburban areas, less common in rural regions | Mostly available in urban areas, gradually expanding to suburban and rural regions | Available virtually everywhere, including rural and remote locations |
| Speed | Slower compared to cable and fiber-optic internet, typically ranging from 1-100 Mbps | Faster than DSL but slower than fiber-optic internet, speeds vary widely but can reach up to 1,000 Mbps (1 Gbps) | Offers the fastest speeds, ranging from 100 Mbps to 10 Gbps, providing ultra-fast connectivity | Slower than cable and fiber-optic internet, speeds range from 12-100 Mbps |
| Connection Type | Utilizes existing telephone lines | Uses coaxial cable infrastructure | Employs optical fibers to transmit data | Relies on satellite signals for connectivity |
| Performance | Performance may degrade with distance from the provider’s central office | Generally consistent performance, less affected by distance than DSL | Consistently high performance with low latency and minimal signal degradation | Performance may be affected by weather conditions and latency due to signal travel distance |
| Cost | Generally more affordable than cable and fiber-optic internet, suitable for budget-conscious users | Typically priced competitively with DSL, offers faster speeds for a slightly higher cost | May be more expensive due to higher speeds and advanced technology, offering better value for performance | Can be more expensive than other options, especially for higher speed plans |
| Installation and Equipment | Easy installation using existing telephone lines, requires a DSL modem | Requires installation of coaxial cable infrastructure, may need a modem or modem-router combo | Requires installation of fiber-optic cables, may include additional equipment such as an optical network terminal (ONT) | Requires installation of satellite dish and modem, may have higher upfront equipment costs |
| Reliability | May experience reliability issues due to older infrastructure and signal interference | Generally reliable, with consistent performance under optimal conditions | Highly reliable with minimal downtime, less susceptible to weather-related disruptions | Reliability may be affected by atmospheric conditions and line-of-sight obstructions |
| Latency | Typically higher latency compared to cable and fiber-optic internet, impacting real-time applications like gaming and video conferencing | Moderate to high latency may affect real-time applications due to signal travel distance | Low latency, ideal for real-time applications such as gaming and video conferencing | Can be more expensive than other options, especially for higher-speed plans |
| Data Caps | Some DSL plans may have data caps, limiting monthly data usage | Some cable internet providers impose data caps on certain plans | Fiber-optic internet plans may offer unlimited data with no caps | Satellite internet plans often have data caps, with options for higher data allowances at additional cost |
Key Factors in Choosing Between DSL and Other Internet Options
Choosing between DSL and other internet options like cable or fiber optic needs thought. What you do online matters when selecting an internet service. For online gaming or video calls, a steady connection is key.
Fiber optic offers fast speeds but isn’t everywhere. DSL uses old phone lines and might be slower. Knowing about cable modems and DSL access multiplexers helps understand costs and speed.
Looking at high bit rate DSL means considering quicker DSL types. It’s about finding a good mix of speed, cost, and what’s available for you or your business.
- Consider Internet Activities: Determine if your internet habits require more bandwidth and higher speed.
- Availability of Technology: Check if fiber optic or high bit rate DSL options are available in your area.
- Equipment Costs: Assess the investment needed for a cable modem or the reliance on a DSL access multiplexer.
- Infrastructure: Reflect on the significance of the central office’s proximity to DSL service quality and speed.
Conclusion
Exploring internet technologies shows DSL’s strong role. Telephone companies upgrade DSL to match new needs, ensuring a mix of good performance and access. DSL providers have cleverly used existing digital loops to connect people, even where fiber isn’t yet available.
DSL stays popular despite new tech. It uses your phone lines for a dedicated, steady service. Even as fiber and wireless networks grow, DSL’s broad use makes it vital. This is especially true in areas without the latest infrastructure.
DSL stands out in the internet tech world. It proves how using established networks can provide stable, budget-friendly services. Even with more wireless options, DSL keeps its value. It offers a dependable connection in the ever-changing digital world.
Author’s Bio:
Scott McAuley is the CEO of TMG Voice. Great teamwork starts with TMG Voice, where all your people, tools, and communication come together for faster and more flexible work.
We offer unparalleled phone service with EPIC support from real humans, no long-term contracts, and the lowest prices with the greatest features. Experience seamless, cost-effective, and personalized telecommunications solutions tailored to your business’s unique needs.
For more information about TMG Voice’s Business Communication services, visit our Plans and Pricing page or contact us using our hotline (832) 862-6900. You can also visit our office at 21175 Tomball Parkway #361 Houston, Texas 77070, or send a message to our email through our Contact Us page.
Compare DSL and Internet Solutions With TMGVoice
Looking to understand the benefits of DSL compared to other choices? Visit our blogs for expert analysis, and check out TMGVoice to explore options that suit your requirements.
Start optimizing your connection today!
FAQ
Is DSL a Landline?
No, DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) is a type of broadband internet connection that uses existing telephone lines to transmit data, but it is not the same as a traditional landline phone service.
What is ADSL Cable Used for?
ADSL (Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) cable is used to provide high-speed internet access over existing telephone lines. It allows users to access the internet while simultaneously using their landline phone service.
What is the Difference Between DSL and Landline?
DSL refers to the technology used for broadband internet access over telephone lines, while a landline typically refers to a traditional wired telephone service that uses copper wires to connect a phone to the telephone network.
What is the Difference Between DSL and Phone Lines?
DSL utilizes phone lines to provide high-speed internet access, while a phone line is a physical connection used to transmit voice signals for telephone communication. DSL uses a separate frequency band on the phone line to carry data without interfering with voice calls.